Understanding Adoption and Its Financial Implications
Adoption, in simple terms, is the legal process through which an adult becomes the permanent parent of a child who is not biologically theirs. While emotionally rewarding, adoption comes with significant financial responsibilities. There are three main types: domestic infant adoption, foster care adoption, and international adoption—each with unique cost structures. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (2023), domestic infant adoption costs range from $20,000 to $45,000, international adoption can exceed $50,000, while adopting through foster care often costs less than $3,000. These figures highlight why financial planning is crucial for adoptive parents, especially when considering long-term obligations like healthcare, education, and housing.
Creating a Comprehensive Pre-Adoption Budget
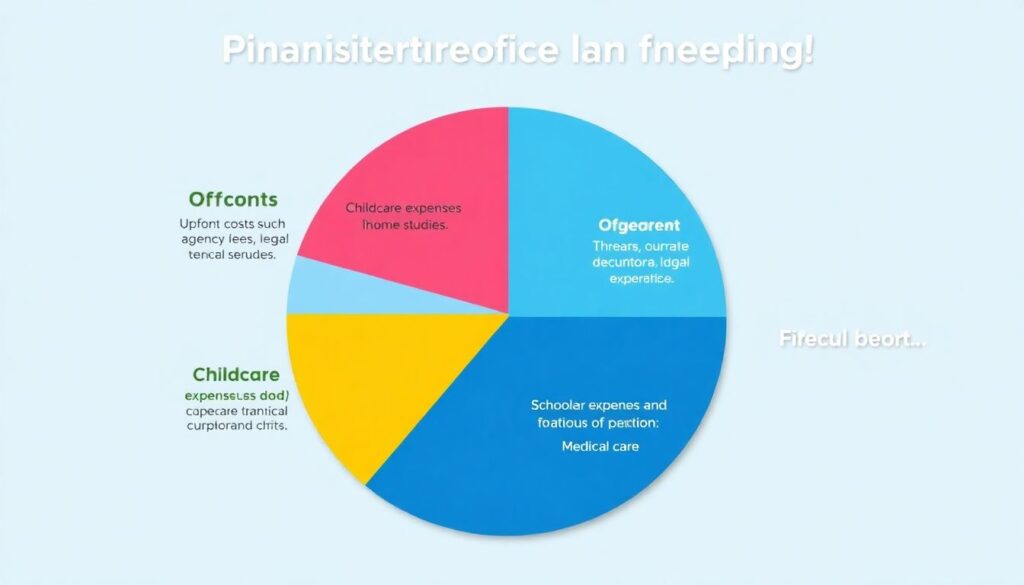
Before even beginning the adoption journey, prospective parents need to set up a detailed financial plan. This includes accounting for upfront costs (agency fees, legal services, home studies) and ongoing expenses (childcare, schooling, medical care). Imagine a pie chart divided into four segments: 30% for legal and agency fees, 25% for travel and lodging (especially for international adoptions), 20% for medical and psychological evaluations, and 25% for post-placement support. Each segment represents a key area where money will go. A comparative look at biological parenting vs adoption shows higher initial costs in adoption but similar long-term spending. For example, while biological parents may pay $15,000 for childbirth in the U.S., adoptive parents might spend double or triple that amount before the child even arrives.
Funding Options and Financial Assistance Programs
The good news is that several funding resources are available to help offset adoption costs. These include the federal adoption tax credit (up to $15,950 in 2023), employer-provided adoption benefits, and grants from non-profit organizations. For instance, the Dave Thomas Foundation offers grants to qualifying families, while organizations like HelpUsAdopt.org provide payments directly to adoption agencies. Crowdfunding is also growing in popularity—platforms like GoFundMe have hosted more than 8,000 adoption campaigns in the past three years alone. Compared to student loans or mortgage financing, adoption grants typically don’t require repayment, making them a more attractive option for families with limited liquidity.
Managing Long-Term Financial Commitments Post-Adoption
Once the adoption is finalized, the financial journey continues. Parents must plan for long-term expenses such as education, healthcare, and extracurricular activities. According to a 2024 report from the USDA, the average cost of raising a child to age 18 in the U.S. is now approximately $284,570—up from $233,610 in 2022, due to inflation and increased healthcare costs. Adoptive families, especially those adopting children with special needs, may also face additional financial responsibilities. For example, therapies or specialized schooling can cost an extra $5,000 to $20,000 annually. Setting up a 529 college savings plan early on or purchasing life insurance tailored to new family structures can help mitigate future financial strain.
Key Financial Planning Steps for Adoptive Parents
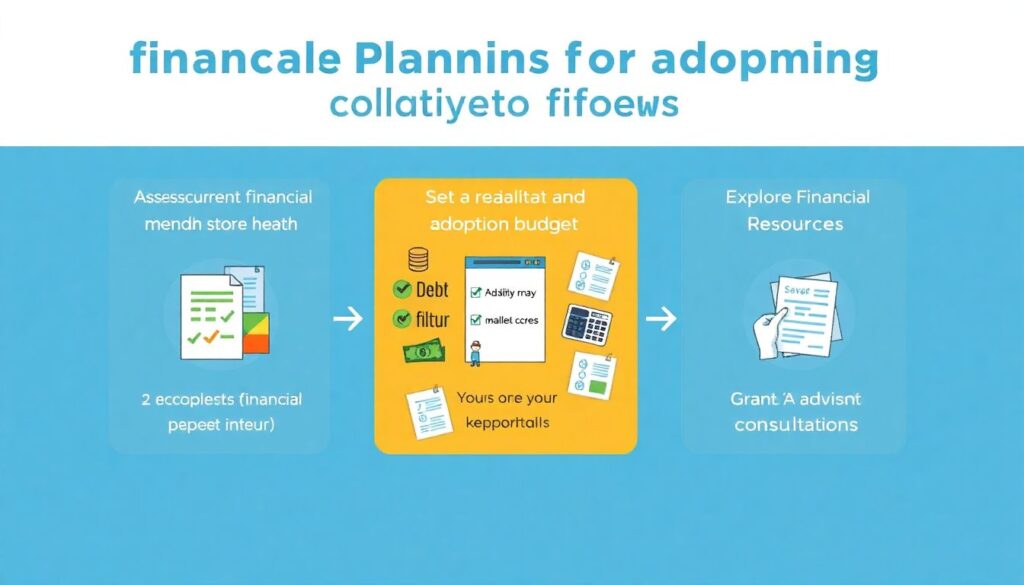
To stay financially secure throughout the adoption process and beyond, parents should follow a structured approach:
1. Assess Current Financial Health – Review savings, debt, credit score, and monthly cash flow.
2. Set a Realistic Adoption Budget – Include both known and variable expenses.
3. Explore All Funding Sources – Apply for tax credits, grants, and employer benefits.
4. Consult a Financial Advisor – Especially one experienced with adoption-related planning.
5. Plan for the Long Term – Establish emergency funds, college savings, and insurance coverage.
Each step ensures that parents not only afford the adoption process but are also prepared for the financial realities of parenting.
Comparing Adoption to Other Major Life Investments
Adoption is often compared financially to other large life events such as buying a home or paying for higher education. While buying a home provides an appreciating asset, adoption is an investment in family and future. Over the last three years, the average cost of a U.S. home rose from $347,500 in 2022 to $391,000 in 2024. In contrast, adoption may not yield financial returns, but it offers emotional and social value that’s hard to quantify. However, the financial risks are real—unforeseen legal complications or failed placements can lead to sunk costs. That’s why risk management, including purchasing legal insurance or working with reputable agencies, is advised.
Conclusion: Planning with Purpose
Financial planning for adoptive parents isn’t just about managing costs—it’s about ensuring stability for the child and peace of mind for the parents. With adoption numbers holding steady at roughly 115,000 annually in the U.S. (per the National Council For Adoption, 2024), the need for informed, strategic financial preparation is more important than ever. By understanding the costs, exploring funding options, and planning for the future, adoptive parents can focus on what truly matters: building a loving and secure home.
